Tech
Google Plans Complete Phase-Out of Universal Analytics by July
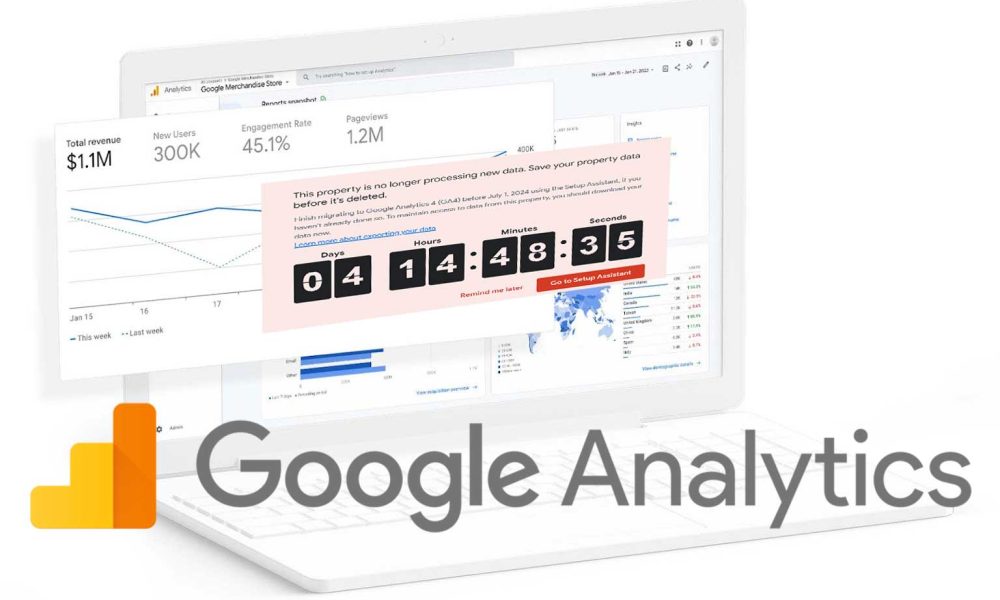
Google Analytics is set to fully retire Universal Analytics (UA) properties on July 1, 2024, completing the transition to Google Analytics 4 (GA4). This follows Google’s earlier announcement of the transition, with the final phase-out meaning all Universal Analytics services and APIs will be inaccessible post-July 1. This significant change impacts millions of businesses and users who have relied on Universal Analytics for web analytics and marketing performance metrics for years.
Key Changes and Actions
Immediate Migration Required:
- Migration Guide: Businesses must transition to GA4 to maintain continuity in their analytics capabilities. The migration guide is available to aid this switch.
- Timeline: Starting July 1, 2024, Google will turn off all Universal Analytics services, making UA properties inaccessible through both the Google Analytics front-end and APIs.
Data Export:
- Export Data Before Deadline: Users should export their UA data before the deadline as Google will delete it after July 1, 2024. Methods for data export are detailed in the Google Analytics Help Center.
- BigQuery Integration: The BigQuery integration for historical data export must be initiated by June 30, 2024. Exported data will remain available in BigQuery, ensuring that users can access their historical analytics data post-transition.
Impact on Integrations:
- Goals and Transactions: Universal Analytics goals and transactions will stop measuring conversions, impacting ad campaigns utilizing Smart Bidding.
- Audience Lists: These will close, affecting media activation and performance in ad campaigns.
- API Requests: All API requests related to UA properties will fail. Tools like Looker Studio will no longer display any UA data.
- Attribution Projects: Attribution projects that were part of the Attribution (beta) in Google Analytics will be deleted.
Context and Benefits of GA4
Enhanced Features:
- Event-Based Tracking: GA4 uses event-based tracking instead of session-based tracking, providing deeper insights into user behavior. This shift allows for more detailed analysis of user interactions and events, making it easier to understand the customer journey.
- Improved Privacy Controls: Enhanced privacy controls and predictive metrics align with modern digital marketing needs. GA4 is designed to adapt to a future with increasing privacy regulations and reduced reliance on cookies.
- Customizable Reports: GA4 offers better agility with customizable reports and faster data access. Users can create tailored reports that meet their specific needs, providing more relevant insights and data visualization options.
Historical Context:
- Initial Announcement: The transition to GA4 was first announced to address the evolving digital landscape and privacy regulations. Google’s decision to phase out Universal Analytics comes as part of a broader strategy to offer more advanced analytics capabilities and ensure compliance with global privacy standards.
- Comparative Advantages: GA4 provides more robust capabilities than its predecessor, UA, making it better suited to the needs of modern digital marketers. With features like AI-powered insights, cross-platform tracking, and enhanced data accuracy, GA4 is positioned as a future-proof solution for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge in their analytics.
Future-Proofing Marketing Efforts:
- Adapting to Privacy Changes: As the digital world moves towards a cookie-less future, GA4’s event-based tracking and focus on first-party data help businesses adapt to these changes while maintaining effective marketing strategies. GA4’s advanced machine learning models can fill in data gaps and provide insights without relying on third-party cookies.
- Integration with Other Google Services: GA4 seamlessly integrates with other Google services, such as Google Ads, Google BigQuery, and Firebase, allowing for a unified view of user interactions across different platforms and devices. This integration enhances the ability to track the full customer lifecycle and measure the impact of marketing efforts more accurately.
Recommendations for Users
To ensure a smooth transition and avoid data loss, businesses and users should:
- Initiate Migration: Follow the GA4 migration guide to transition from UA to GA4. Google provides detailed instructions and support to help users migrate their existing setups and configurations to the new platform.
- Export Data: Export historical data from UA using the methods provided by Google, and for UA 360 users, ensure the BigQuery export is completed by June 30, 2024. Regular data backups can help safeguard against potential data loss during the transition.
- Update Integrations: Modify integrations to be compatible with GA4 to maintain ad campaign performance and analytics capabilities. Businesses should review their current integrations and make necessary adjustments to ensure seamless data flow and functionality with GA4.
- Educate Teams: Train teams on the new features and capabilities of GA4 to maximize its potential. Investing in training and development can help teams leverage GA4’s advanced features and gain deeper insights into customer behavior.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of GA4 and optimize settings to align with business goals. Regularly reviewing analytics data and making data-driven decisions can enhance marketing strategies and improve overall performance.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Learning Curve: Adapting to GA4 may require a learning curve for users familiar with UA. Google offers various resources, including tutorials, webinars, and support documentation, to assist users in understanding and utilizing GA4 effectively.
- Data Discrepancies: Users may notice discrepancies between UA and GA4 data due to differences in tracking methodologies. It’s essential to understand these differences and adjust expectations accordingly.
- Customization Needs: Businesses with heavily customized UA setups may need to invest additional time and resources to replicate similar configurations in GA4. Custom events, dimensions, and metrics should be carefully mapped to ensure consistency in reporting.
Success Stories and Case Studies:
- Early Adopters: Many early adopters of GA4 have reported significant improvements in their analytics capabilities and business insights. Case studies highlight successful transitions and the benefits of GA4’s advanced features in driving marketing performance and operational efficiency.
- Industry Examples: Various industries, including e-commerce, finance, and media, have successfully implemented GA4 to gain a competitive edge. Real-world examples demonstrate how GA4’s enhanced tracking and reporting capabilities can lead to better decision-making and improved customer experiences.
Conclusion: The transition from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 represents a significant shift in the way businesses track and analyze user data. While the change may come with challenges, the benefits of GA4’s advanced features, improved privacy controls, and future-proof capabilities make it a worthwhile investment for businesses looking to stay ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape. By proactively migrating to GA4, exporting historical data, and updating integrations, businesses can ensure a seamless transition and continue to leverage powerful analytics to drive growth and success.